Introduction
Pervasive environments present many new opportunities to incorporate a wide variety of fixed and mobile devices, sensors, and actuators into next generation distributed services and applications. Application context in pervasive environments can be highly volatile with changing location, devices, fixed and wireless network connectivity and QoS, power levels, security requirements. Additionally user and system preferences, and user collaborative situations may also change.
PACE infrastructure research focuses on the programming toolkits, paradigms, and development tools required to effectively create seamless, context-aware applications in pervasive environments, building on the PACE context, preference, and programming models. This research addresses the foundations necessary to develop pervasive application components that exhibit autonomic (self-governing, self-adapting, self-optimising) behavior. This allows for applications that dynamically adapt to available resources, appear well behaved to users, and do not present unmanagable interaction or configuration burdens for users and administrators.
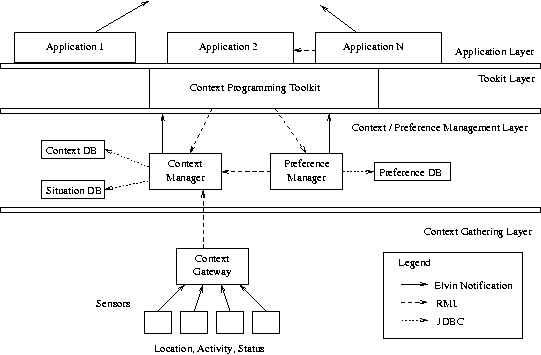
The infrastructure is organised into three layers:
- Context Gathering:. This layer acquires context information from various sensors and devices. The information is processed using interpretation and data fusion.
- Context and Preference Management: The context manager stores context information as facts and maintains descriptions of higher-level context situations. The preference manager stores user and system preferences which can be evaluated against context instances.
- Context Programming Toolkit: This layer provides application interfaces for the PACE triggering and branching models, access to the context and preference managers, distributed messaging, and other utilities for pervasive environments.
Impact
The results of this research support the development of pervasive, context-aware applications that can exhibit robust, autonomic behavior in highly dynamic environments. By providing runtime support for the PACE context and preference managers, as well as the programming models, context handling logic may be separated from application logic. Context and preference models may then evolve independently of applications. Applications benefit from new context and preference models without code changes.